- 14 September 2023
- No Comment
- 1448
Exploring the Best Student Loan Options for USA Students

I’m Nabeel, a seasoned Chartered Accountant with a remarkable 17-year journey through the worlds of investment banking, management consulting, and entrepreneurship. As someone well-versed in financial matters, I understand the importance of making informed decisions when it comes to funding your education. In this article, I’ll leverage my expertise to guide you through the intricacies of federal and private student loans, helping you gain valuable insights as you seek the best loan providers in the USA.
Types of Student Loans
Student loans are a critical aspect of achieving academic goals, and they come in two main forms: federal and private loans.
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. Department of Education and are typically more advantageous for students due to their borrower-friendly terms. There are three main types of federal student loans:
Direct Subsidized Loans
These loans are based on financial need, and the government pays the interest while the borrower is in school, during the grace period, and deferment. They are available to undergraduate students.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans
These loans are not need-based, and interest accrues on the loan from the time it’s disbursed. Undergraduate, graduate, and professional students can qualify for these loans.
PLUS Loans (Parent or Graduate)
PLUS loans are available to parents of dependent undergraduate students and graduate or professional students. These loans are not need-based and can cover the remaining cost of education after other financial aid has been applied. However, they require a credit check, and the borrower must not have an adverse credit history.
Private Student Loans
Private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and online lenders. They come with terms and conditions set by the lender, and eligibility criteria may vary. These loans are not subsidized by the government and often require a creditworthy co-signer for students with a limited credit history.
Here are some key characteristics of private student loans:
Credit-Based
Private student loans often require a credit check, and the interest rates and terms are determined based on the borrower’s creditworthiness. Students with limited credit history may need a cosigner, such as a parent or guardian, to qualify for a private loan.
Variable or Fixed Interest Rates
Private loans may offer both variable and fixed interest rate options. Variable rates can change over time, while fixed rates remain constant throughout the life of the loan.
Loan Limits
Private loans typically have higher borrowing limits compared to federal student loans, allowing students to potentially cover the full cost of attendance, including tuition, fees, housing, and other educational expenses.
Repayment Terms
Repayment terms for private loans vary by lender but are typically less flexible than federal loans. Borrowers may have fewer options for income-driven repayment plans or loan forgiveness.
Cosigner Release
Some private lenders offer cosigner release options, allowing borrowers to remove the cosigner from the loan after meeting specific requirements, such as making a certain number of on-time payments.
Eligibility Criteria
Private lenders may have their eligibility criteria, which can vary from one institution to another. This may include minimum credit score requirements, income verification, and citizenship status.
Best Private Student Loan Providers
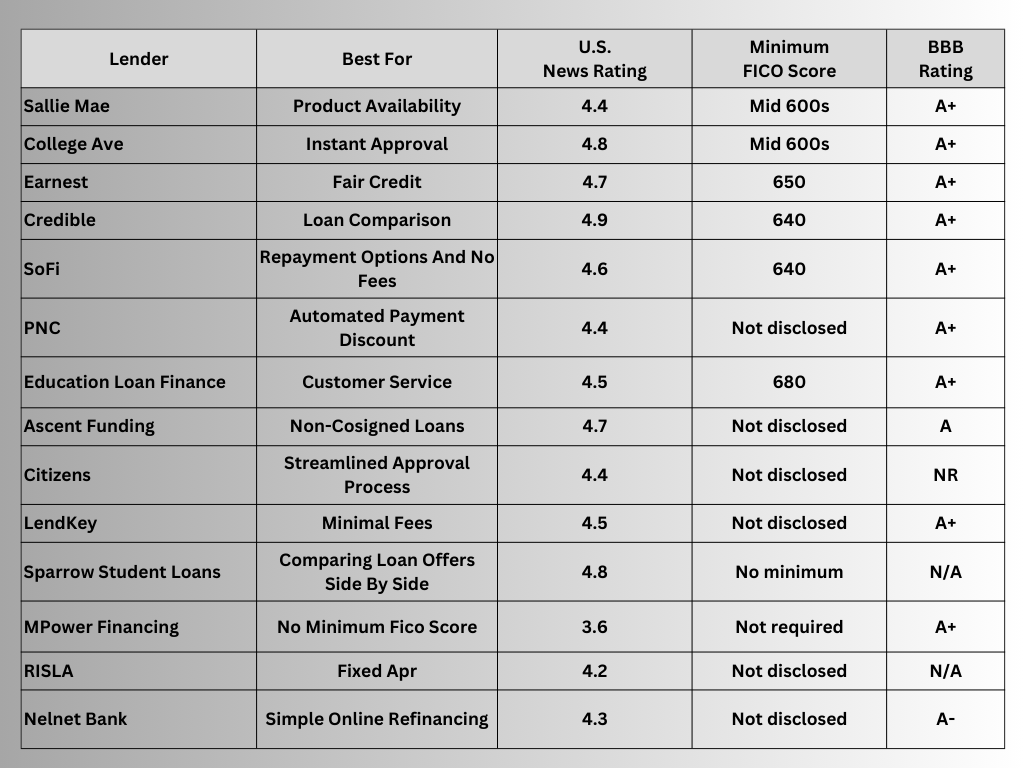
BBB stands for the Better Business Bureau, which is a non-profit organization that evaluates and rates businesses based on their ethical practices, customer complaints, and overall business conduct. The BBB assigns ratings ranging from A+ (the highest) to F (the lowest) to indicate the level of trustworthiness and customer satisfaction associated with a business.
U.S. News & World Report is a widely respected media organization known for its annual rankings and reviews of various institutions and services, including colleges, universities, and financial products. The U.S. News Rating in this context refers to their evaluation and ranking of private student loan providers based on factors such as interest rates, loan terms, customer satisfaction, and other criteria. A higher U.S. News Rating suggests that a lender has been evaluated positively by the publication and maybe a more reputable or competitive option.
Pros and Cons of Federal Student Loans 
Pros:
Low Fixed Interest Rates: Federal loans typically offer lower fixed interest rates compared to private loans, making them more affordable in the long run.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans: Federal loans offer income-driven repayment plans that adjust monthly payments based on the borrower’s income, making them more manageable.
Loan Forgiveness Programs: Some federal loans may be eligible for forgiveness programs, such as Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF).
Cons:
Limited Borrowing Amounts: Federal loans have borrowing limits, which may not cover the full cost of attendance for some students.
Interest Accrual: Unsubsidized federal loans accrue interest while in school, increasing the total repayment amount.
Strict Eligibility Criteria: Eligibility for federal loans depends on factors like financial need, which may exclude some students.
Pros and Cons of Private Student Loans
Pros:
Flexible Loan Amounts: Private loans often allow borrowers to cover the full cost of attendance, including tuition, housing, and books.
Cosigner Options: Students with a limited credit history can qualify with a cosigner, potentially securing a lower interest rate.
Quick Approval: Private loans typically have a faster application and approval process compared to federal loans.
Cons:
Higher Interest Rates: Private loans usually have higher interest rates, leading to more significant long-term costs.
No Income-Driven Repayment: Private lenders may not offer income-driven repayment plans, making payments less flexible.
Lack of Forgiveness Programs: Private loans do not typically offer loan forgiveness options, putting borrowers at a disadvantage.
Compare Federal and Private Student Loans
When choosing between federal and private student loans, it’s essential to consider your circumstances and priorities. Here’s a brief comparison:
Interest Rates: Federal loans often offer lower fixed interest rates, while private loans may have variable rates that can be higher.
Repayment Options: Federal loans provide income-driven repayment plans, deferment, and forbearance options, while private loans have less repayment flexibility.
Cosigner Requirement: Private loans may require a cosigner if the student has a limited credit history, while federal loans do not.
Loan Forgiveness: Federal loans offer forgiveness programs, while private loans do not typically provide this benefit.
How Students Can Maximize Federal and Free Financial Aid
Maximizing federal and free financial aid is essential for students to minimize the need for student loans and reduce the overall cost of their education. Here are several strategies to help students make the most of available financial aid opportunities:
Complete the FAFSA Early:
The Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) is the gateway to federal and many state-based financial aid programs. It’s crucial to submit the FAFSA as soon as possible after it becomes available each year, typically on October 1st. Some aid programs have limited funds, so early submission increases your chances of receiving aid.
Explore Federal Grants
Federal grants, such as the Pell Grant, are typically awarded based on financial need and do not require repayment. Make sure you meet all eligibility criteria and apply for these grants through the FAFSA.
Search for Scholarships
Look for scholarship opportunities from various sources, including your college or university, private organizations, and foundations. Scholarships are essentially free money and can significantly reduce your educational expenses.
Check State-Based Aid
Many states offer financial aid programs for residents pursuing higher education. Research and apply for state-based grants, scholarships, and tuition assistance programs.
Consider Work-Study
Federal Work-Study provides part-time job opportunities for students with financial need. These jobs can help cover your educational expenses while gaining valuable work experience. Check with your school’s financial aid office for available positions.
Meet with a Financial Aid Advisor
Schedule a meeting with your college’s financial aid advisor to discuss your financial situation and explore all possible aid options. They can provide guidance on available programs and help you navigate the financial aid process.
Maintain Satisfactory Academic Progress
Many financial aid programs require students to maintain a minimum GPA and complete a certain number of credit hours each semester. Failing to meet these requirements can result in the loss of financial aid eligibility.
Maximize Tax Benefits
Take advantage of educational tax credits and deductions, such as the American Opportunity Tax Credit (AOTC) and the Lifetime Learning Credit, to reduce your tax liability.
Selecting the best loan provider for your education is a crucial decision. Federal loans are generally more advantageous for their borrower-friendly terms, but private loans can be a viable option for students with specific financial needs. It’s essential to weigh the pros and cons carefully and explore all available options before committing to a loan. By understanding the differences between federal and private student loans, you can make a well-informed choice that sets you on the path to academic success without unnecessary financial burden.

