- 18 September 2023
- No Comment
- 762
Case Study of The Infamous Toyota Recall Crisis of 2010

I’m Nabeel — a seasoned Chartered Accountant with a remarkable 17-year journey through the worlds of investment banking, management consulting, and entrepreneurship. In this case study, we will delve into the infamous Toyota Recall Crisis of 2010, examining its historical context, the root causes of the crisis, its financial impact, and the strategic solutions that helped Toyota regain its standing in the automotive industry.
History of Toyota: Pioneering Excellence in Automobiles
In the early 20th century, Japan was on the cusp of an industrial revolution, and a visionary named Kiichiro Toyoda played a pivotal role in shaping its future. In 1937, Kiichiro Toyoda founded Toyota Motor Corporation, following in the footsteps of his father, Sakichi Toyoda, a renowned inventor. Toyota’s journey began with the intent to create automobiles that would revolutionize the industry, not only in Japan but worldwide. This marked the inception of a legacy known for innovation, quality, and reliability.
Kiichiro Toyoda: A Visionary Leader

Kiichiro Toyoda, the son of Sakichi Toyoda, was born on June 11, 1894, in Japan. He inherited his father’s passion for innovation and manufacturing. Under Kiichiro’s leadership, Toyota began producing its first passenger car, the Model AA, in 1936.
His commitment to quality and efficiency laid the foundation for Toyota’s renowned Production System (TPS), a model of manufacturing excellence that continues to influence industries globally.
Recalls by Major Automakers
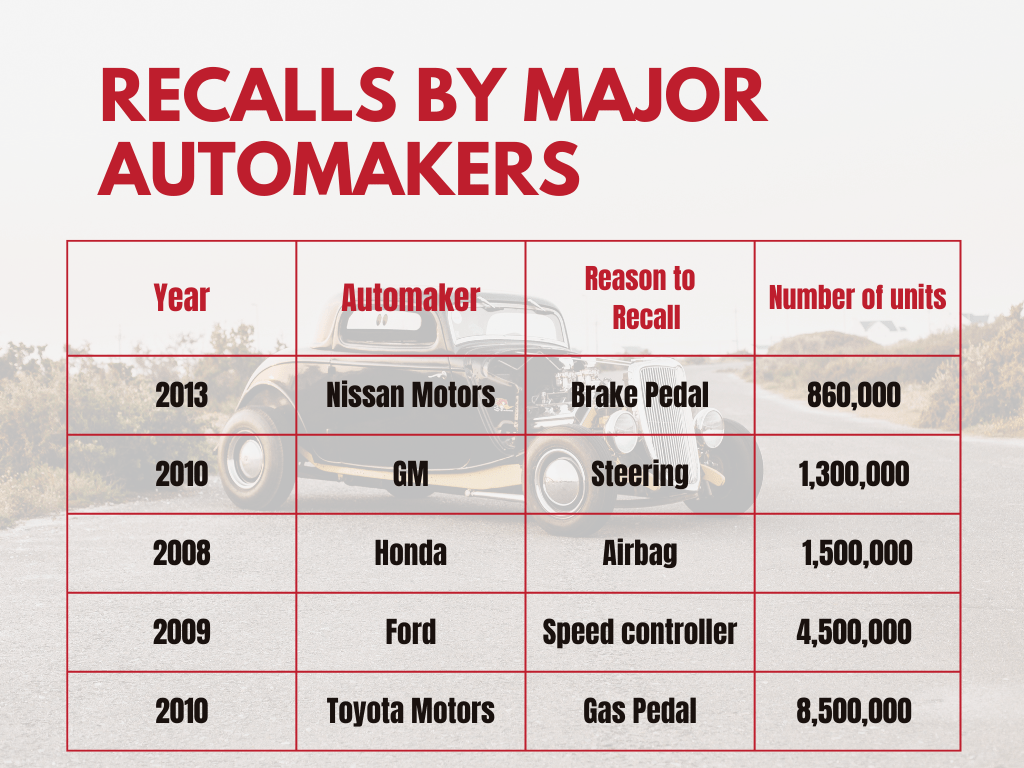
The Crisis of 2009 to 2011 Toyota Vehicle Recalls
As we dive into the heart of the matter, it becomes clear that Toyota’s recall crisis from 2009 to 2011 was a turning point in the company’s history.
- The scope of the crisis was immense, affecting more than 8.5 million vehicles globally.
- The total number of recalls surpassed 10 million units, spanning various Toyota models.
- This crisis took a substantial financial toll on Toyota, with an estimated cost of approximately $2 billion.
The focal point of this crisis was the issue of unintended acceleration, where vehicles experienced sudden and unexpected acceleration without any input from the driver. These occurrences led to numerous incidents and accidents, raising serious concerns about the safety of Toyota vehicles.
The exact number of incidents and casualties can vary depending on different sources and investigations. Toyota acknowledged and addressed these cases as part of their recall and safety improvement efforts. The media spotlight and public scrutiny compounded the urgency for Toyota to address these issues comprehensively and swiftly.
Root Causes of the Company’s Problems: What Went Wrong
To gain a holistic understanding of this crisis, it’s imperative to examine the root causes that contributed to Toyota’s predicament:
- Technical Issues: Investigations revealed that sticky accelerator pedals and improperly placed floor mats were the culprits behind unintended acceleration.
- Communication Gap: Toyota was heavily criticized for its slow and inadequate response to reports and allegations, leading to a significant communication gap.
- Regulatory Pressure: Regulatory agencies, particularly the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, conducted investigations that further intensified the crisis.
Possible Alternatives to Address the Causes: A Path Forward
In hindsight, Toyota could have explored various alternatives to address the issues:
- Improved Quality Control: Enhancing quality control processes in manufacturing could have prevented technical issues at the source.
- Effective Communication: A more proactive, transparent communication strategy with regulators and customers could have mitigated the impact of recalls.
- Regulatory Compliance: Stricter adherence to regulatory standards would have reduced the legal and financial risks associated with the crisis.
The Financial Impact of the Toyota Recall Crisis
- Sales dropped by 16% in January 2010 due to safety concerns, a significant decline not seen in a decade.
- Toyota’s stock price fell by about 10% overall and 30% compared to the S&P 500 index from September 2009 to April 2010. In contrast, Ford’s stock price increased by 80% during the same period.
- The Wall Street Journal estimated Toyota’s financial impact at over $5 billion for the next fiscal year, covering litigation, warranty costs, increased marketing, and incentive campaigns.
- Initial recall costs were approximately $2 billion, but future expenses, including potential litigation settlements, could reach up to $5.5 billion.
- Fitch placed Toyota’s “A+” credit rating on negative watch, potentially increasing borrowing costs.
- Toyota agreed to pay a $16.4 million fine to the NHTSA for delaying recalls.
- Despite the financial toll, Toyota reported a $1.2 billion profit for Q4 and $2.2 billion for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2010. However, recall expenses amounted to $1.1 billion, with a global sales loss of $800 million, and a $233 million operating loss in the North American region.

Solutions and Plan of Action: Restoring Trust
Toyota’s enduring commitment to quality, safety, and innovation ultimately proved to be the cornerstone of its recovery. By diligently addressing the root causes of the recall crisis, improving communication strategies, and fostering a corporate culture of accountability, Toyota managed to rebuild its reputation and reassert its position as an industry leader.
Toyota initiated a comprehensive plan of action to rebuild its reputation and regain customer trust. Here are some of the key actions taken by Toyota:
Recall and Repairs
Toyota initiated a comprehensive recall of affected vehicles to address the technical issues responsible for unintended acceleration. This involved fixing or replacing the faulty accelerator pedals and floor mats that were causing the problem.
Management Changes
The company replaced its President, Akio Toyoda, and implemented structural changes to improve internal communication and decision-making processes. These changes aimed to ensure a more proactive and responsive approach to quality and safety issues.
Quality Control
Toyota significantly increased its focus on quality control and safety measures within its manufacturing processes. The company implemented rigorous testing and quality assurance protocols to identify and address potential design flaws before they could become widespread issues.
Transparency
Enhancements in transparency and openness in communication with regulators, customers, and the public were prioritized. Toyota began sharing more information about its decision-making processes, safety measures, and recall progress with stakeholders.
Collaboration with Regulatory Agencies
Toyota worked closely with regulatory agencies, particularly the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States, to address safety concerns and regulatory compliance. This collaboration aimed to ensure that Toyota’s vehicles met and exceeded safety standards.
Enhanced Safety Features
Toyota introduced new safety features in its vehicles to prevent unintended acceleration and enhance overall safety. These included brake override systems and smart throttle technology, which could reduce the risk of sudden acceleration incidents.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Toyota launched public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the safety measures and improvements implemented in its vehicles. These campaigns aimed to rebuild consumer trust and confidence in the brand.
Continuous Improvement
Toyota embraced a philosophy of continuous improvement (kaizen) across its operations, including quality control and safety measures. The company committed to learning from the recall crisis and implementing ongoing improvements to prevent similar issues in the future.
Through these efforts, Toyota not only recovered from the crisis but also strengthened its position in the automotive industry. The company’s enduring commitment to quality, safety, and innovation allowed it to rebuild its reputation and reassert its position as a leader.
Lessons in Resilience
The Toyota recall crisis of 2010 offers a profound lesson for organizations worldwide. Despite facing monumental challenges, Toyota emerged from the crisis with its legacy of innovation and commitment to excellence unscathed, a testament to its enduring values and unwavering vision.
Key Lessons from the Toyota Recall Crisis (2010):
- Safety and Quality First: Prioritize safety and quality to avoid reputational and financial damage.
- Transparent Communication: Timely and transparent communication builds trust during crises.
- Effective Crisis Management: Swift action and leadership accountability are vital for crisis resolution.
- Continuous Improvement: Embrace a culture of improvement to prevent issues from escalating.
- Collaboration with Regulators: Work closely with regulators for compliance and safety.
- Consumer Trust: Regaining consumer trust is challenging once lost; safeguard it at all costs.
- Long-Term Focus: Maintain a long-term perspective and stay committed to core values.
- Learn from Mistakes: Crises are learning opportunities; use them to enhance processes.
- Brand Resilience: Resilience in adversity strengthens brand reputation and credibility.
Conclusion: Toyota’s Resilience and the Road Ahead
In conclusion, as a seasoned management consultant, I believe the Toyota crisis of 2010 serves as a powerful reminder of the importance of safety, quality, and transparent communication, especially during crises. The key lessons from this experience are effective crisis management, leadership accountability, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Despite the significant financial impact of the recalls, Toyota reported a profit of $1.2 billion for the fourth fiscal quarter and $2.2 billion for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2010. This demonstrated the company’s financial resilience.
Toyota’s resilience showcases the enduring value of brand reputation and long-term vision. As businesses strive for excellence and innovation, core values, customer satisfaction, and safety must always be at the forefront.
In today’s dynamic business landscape, these lessons guide us in building enduring organizations that emerge stronger and more resilient from challenges, upholding the principles of accountability, quality, and trustworthiness.
Let’s apply these lessons as we navigate our paths to success, ensuring safety, quality, and transparent communication at every step, forging a future where our organizations thrive and legacies endure.



