- 8 August 2022
- No Comment
- 154
Intro to the different classes of vaccines and their after-effects
The vaccine has become a household matter of discussion after the start of the Covid-19 pandemic. But very few people have little knowledge of what a vaccine is composed of. The basic question which arises is what the vaccine is. It’s a transparent form of dose that can help in preventing viral diseases and infections. It’s a mode of medication that is used for prevention instead of treatment. When a body catches an infection, the body first starts showing symptoms of the disease. That’s the best stage where the infection can be stopped from further spreading.
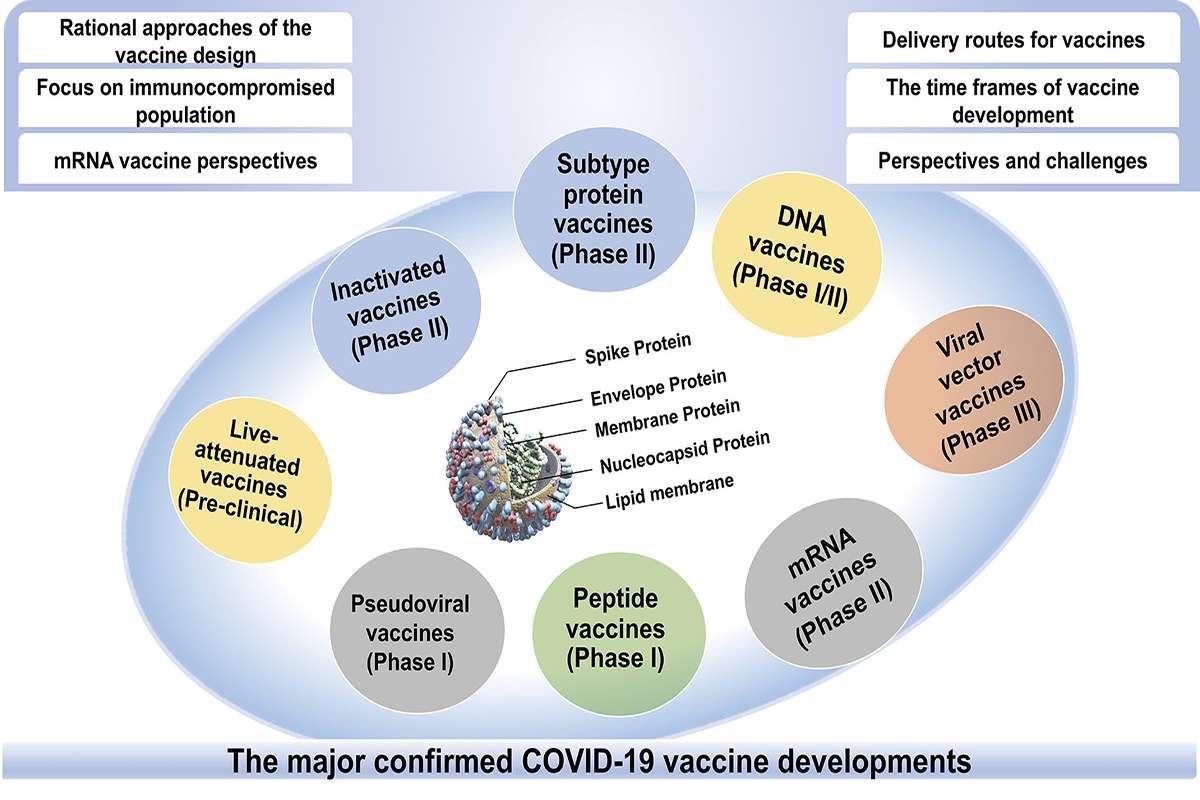
Fundamentally, the vaccine triggers an immune response to the disease or infection, that the body encounters for the first time. It’s sort of assistance to the body in developing accurate antibodies inside the body itself. The vaccine works on the principle of recognizing the pathogen, which is a specific agent in the shape of a virus or bacteria which causes disease. After recognition of the pathogen, the immune system would efficaciously eradicate it. Vaccines have many types and depend on the nature of the disease. Some of the main vaccines are explained below:
1. Whole Pathogen Vaccines:
This vaccine is one of the oldest and most renowned vaccination methods. The immune response stimulates against the pathogen which is naturally caused by the entire disease. The whole disease-caused pathogen is dangerous for the body to have it. It can increase the risk of virus dispersal inside the whole body. The modern vaccine can be used for the alteration of this vaccine.
2. Live Attenuated Vaccines:
In this vaccine, the pathogen is attenuated inside the body hence developing the credible immune system to protect the body from the disease. The term attenuated means to weaken. The idea acquired here is to weaken the pathogen to eliminate it. This modification of pathogens can be a natural phenomenon or development of modern scientists. This vaccine can be extremely beneficial for the body having a good immune system. People with poor immunity rather get the undesired outcome of this vaccine due to the concept of weakening the pathogen. The weakened virus can be the reason for the multiplication of bacteria in the body.
3. Inactivated Vaccines:
The vaccine kills the whole virus inside the body but it doesn’t have long-lasting effects as in the live attenuated vaccine case. It can be used in people with a lack of immune power because it doesn’t replicate the virus within the body.
4. Subunit Vaccines:
It doesn’t contain the whole virus of bacteria like other vaccines. Instead of that, it contains one or more antigens from the surface of the pathogens which only focus on the virus specifically.
5. Toxoid Vaccines:
The immune system detects the toxin generated from the surface of the pathogens. These toxins are not poisonous or harmful to the body and can be used in the formation of a protective layer against the virus.
6. Recombinant protein vaccines:
These vaccines modify the yeast cell to transform it into tough surface protein that prevents the disease. A general DNA is taken from the virus or bacteria from which we want to protect the body which is then transferred to the yeast cell for transformation as an active ingredient in these types of vaccines.
7. Conjugate Vaccines:
As the name suggests these vaccines are prepared from a combination of different elements. With this vaccine, immunity can be achieved through the conjugation of viruses or bacteria to the polysaccharides which are complex sugars on the surface of bacteria rather than proteins. The polysaccharides are conjugated with diphtheria or tetanus toxoid protein to create a strong immune response.
8. Nucleic acid vaccines:
These vaccines don’t deliver antigens within the body but renovate the cell of the body into an antigen. Its basic principle is to generate genetic training and command of antigens to the cell in the body to stimulate the immune response in contrast to bacterial or viral infections.
9. Viral Vectored Vaccines:
Like nucleic acid vaccines, these vaccines are the output of the latest biotechnological research. The vaccine uses an inoffensive virus to transport genetic code to the antigen in the cell of the body. Next, the vaccine constructs proteins for the stimulation of immune retort. It is fully fledged into the cell lines and would be cheaper as compared to nucleic acid vaccines.
The vaccines have possible after-effects that can be undesirable for the one who gets vaccinated. The adverse effects of the vaccines can be different from one person to the next. It depends on the immune system of a body. The common effects after the vaccination are general pain or sore arm on the injected part of the arm or whole arm. Slight fever can also be caused due to the immune response or stimulation to the pathogen which is not hazardous to the health.



