- 11 November 2023
- No Comment
- 1612
Uber’s Journey: How a Simple Idea Turned into a Multi-Billion Dollar Business

From a Taxi Problem to a Global Solution
Uber has grown from a small startup to a global phenomenon. Uber operates in more than 10,000 cities across 72 countries, serving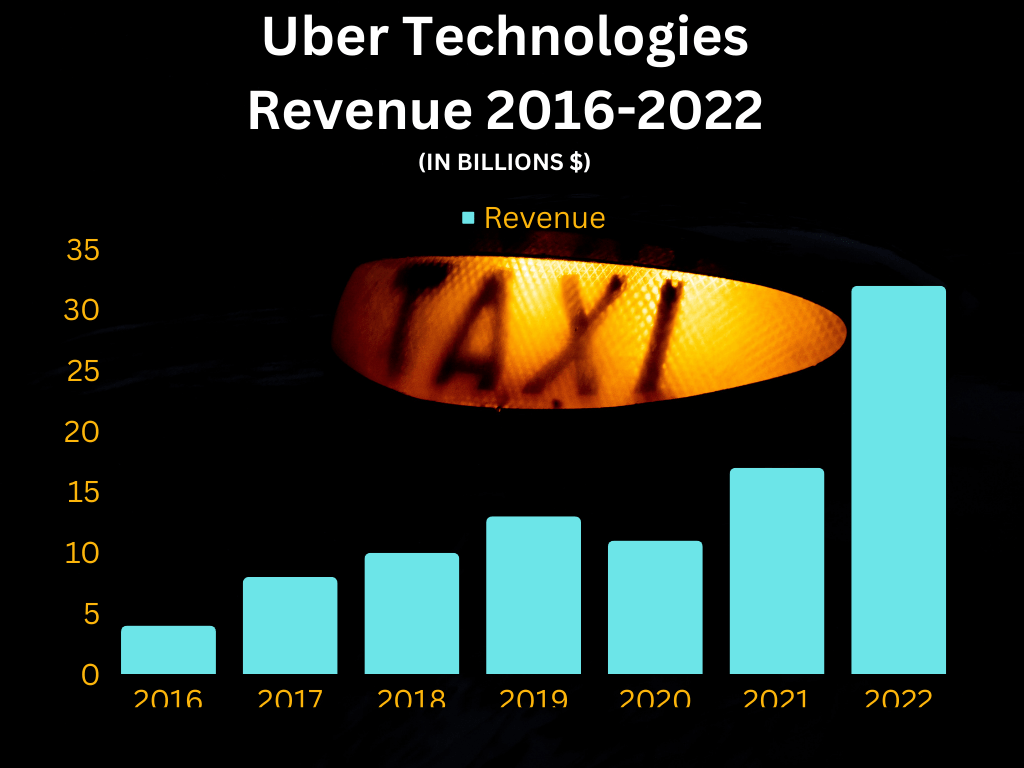 over 130 million monthly active users and completing over 7.6 billion trips, more than the previous record of 6.9 billion trips in 2019. In 2022, Uber Technologies reported a net revenue of 32 billion U.S. dollars, an 82% rise from the previous year.
over 130 million monthly active users and completing over 7.6 billion trips, more than the previous record of 6.9 billion trips in 2019. In 2022, Uber Technologies reported a net revenue of 32 billion U.S. dollars, an 82% rise from the previous year.
Uber is a company that connects people who need a ride with drivers who have their own cars. Uber’s app lets you see the nearest available drivers, their arrival times, and their ratings. Uber app can also help track rides in real-time and enable users to pay with a credit card or other online payment methods.
Investments from big names
In 2010, Uber raised a modest $1.25 million from some angel investors. The next year, Uber’s growth rate skyrocketed, and it secured $11 million from Benchmark Capital and others. By December 2011, Uber had attracted $37 million from big names like Goldman Sachs, Menlo Ventures, and Amazon’s Jeff Bezos.
In August 2013, Uber entered the Indian market, where it faced stiff competition from Ola, a local rival. Uber also received a massive $258 million investment from Google Ventures, which boosted its valuation to $3.76 billion.
In 2014, Uber set its sights on China, hoping to tap into the huge potential of the world’s most populous country. However, Uber met its match with Didi Chuxing, a dominant Chinese player. After two years of fierce battles, Uber and Didi Chuxing decided to merge in August 2016. Uber also raised $3.5 billion from Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund.
In 2015, Uber achieved a remarkable milestone: it completed its 1 billionth trip.
But how did Uber compete in a highly competitive and regulated industry? What are the challenges and opportunities that Uber faced along the way? And what are the lessons that aspiring entrepreneurs can learn from Uber’s journey?
Uber: How Two Entrepreneurs Turned a Taxi Problem into a Global Solution
Have you ever been stuck in a city, unable to find a taxi? That’s what happened to Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp, two entrepreneurs from San Francisco, in 2009. They were in Paris on a cold and snowy night, and they couldn’t get a cab. They wished there was a better way to get around the city.
San Francisco, in 2009. They were in Paris on a cold and snowy night, and they couldn’t get a cab. They wished there was a better way to get around the city.
Idea!
They had an idea: what if you could use your phone to request and pay for a fancy car? They were inspired by the private car services they had seen in Paris and other European cities.
They created a service that did just that. They launched it in June 2010 in San Francisco with a few black cars. They named it UberCab, which means “above” or “superior” in German. The service was a hit among people who liked the convenience and reliability of the app.
But not everyone was happy with UberCab. Traditional taxi services and local government authorities said that UberCab was breaking the rules for transportation services. UberCab hired lawyers and lobbyists to help them deal with the complex regulations and build support for their service.
In 2011, UberCab expanded its service to New York City, and the company continued to grow fast over the next few years, reaching other cities in the United States and around the world.
From Ubercab to Uber
In 2013, UberCab changed its name to just “Uber” and started to focus more on its ride-sharing service, which lets drivers use their own cars to give rides to users. This new model was very successful, and the company expanded its operations even more.
Uber is now one of the largest ride-hailing services in the world, operating in more than 10,000 cities across 72 countries. Uber has changed the way people travel by offering a more convenient and efficient alternative to traditional taxi services.
Uber: How It Became More Than Just a Ride-Hailing Service
Uber started as a service that let people request and pay for fancy cars using their phones. But Uber is not just a ride-hailing service. Uber has also added other transportation options, such as:
- Uber Eats: lets users order food from local restaurants and have it delivered by Uber drivers.
- Uber Freight: a service that matches shippers with carriers who can transport their goods by truck.
- Uber Elevate: a project that aims to develop flying taxis that can provide fast and affordable urban air transportation.
Uber made $32 billion in 2022; $14 billion in revenue came from ride-hailing and $10.9 billion from mobility; the rest was from freight services.
Uber has used technology and data to improve its operations. It has used dynamic pricing to adjust fares based on demand and supply, ensuring service efficiency. It has used GPS, maps, and algorithms to match riders and drivers, calculate routes, and estimate trip details.
Uber has also invested in innovation, exploring new technologies such as self-driving cars, electric bikes, scooters, flying taxis, and delivery drones. It has envisioned a future of accessible, sustainable urban mobility.
Uber Business Model: How Uber Turns Your Car into a Money-Making Machine
Uber is not just for riders. Uber is also for drivers. Uber’s business model is based on the sharing economy, where people can make money by sharing unused assets, such as cars. The platform lets the Uber driver sign up and Uber login at any time and start making money by giving rides to users, who pay based on how far and how long the ride is. Here are the main parts of Uber’s business model:
Technology Platform
Uber’s platform connects drivers and users through its mobile app. The app lets users request rides, see their driver, and pay for the ride without using cash.
Dynamic Pricing
Uber uses a dynamic pricing model called “surge pricing,” which changes the price of a ride based on supply and demand. When there are more people who want rides than drivers who can give them, prices go up to encourage more drivers to get on the road.
Driver Network
Uber’s driver network is a key part of its business model. Drivers can join the platform and start making money by giving rides. The company also gives incentives and bonuses to drivers to keep them happy and loyal.
User Experience
Uber focuses on the user experience, giving users a convenient and hassle-free way to get around. The company uses data and analytics to improve its service and customize the user experience.
Expansion
Uber has grown fast into new markets and has added more services besides its original ride-hailing service. The company now offers food delivery through Uber Eats and has invested in other transportation options, like electric bikes and scooters.
Partnership and Integration
Uber partners with different businesses to add more services and improve the customer experience. For example, the company has partnered with airlines to let users book Uber rides directly from their airline’s app.
Uber Revenue Model: How Uber Makes Money from Each Ride
Uber makes money by taking a percentage of the total fare that the rider pays for each ride. Uber’s percentage depends on the location, but it is usually between 20% and 30% of the total fare.
Here are some of the main ways that Uber makes money from each ride:
Commission
This is the main way that Uber makes money. Uber takes a commission on each ride that is completed through its platform. The commission percentage varies by location and can be between 20% and 30% of the total fare that the rider pays.
Surge Pricing
Sometimes, when there are more people who want rides than drivers who can give them, Uber increases the fare that the rider pays. This is called surge pricing, and it helps Uber make more money from each ride. Surge pricing also encourages more drivers to get on the road so that riders can get a ride when they need it.
Fees
Uber also charges different fees to both riders and drivers. For example, Uber may charge a booking fee, an airport fee, or a service fee to drivers. These fees help Uber cover its costs and make more money from each ride.
Subscription Services
Uber offers a subscription service called Uber Pass, which gives users discounts on rides and other benefits. Users pay a monthly fee to join Uber Pass, and this helps Uber make more money from each ride.
Other Services
Uber also offers other services besides its main ride-hailing service. For example, Uber offers food delivery through Uber Eats and freight shipping through Uber Freight. These services make money by charging fees to restaurants, riders, and other partners.
Advertising
Uber also makes money by advertising on its platform. Uber allows businesses to advertise on its app and makes money by charging them advertising fees.
Challenges That Affect Uber Business
Uber faces many challenges that can affect its business, its money, and its success. Here are some of the main problems that Uber is facing right now:
Uber Legal and Regulatory Problems
Uber’s business has faced a lot of problems from the authorities. Many governments and regulators have said that Uber’s business model is illegal and unfair. They have tried to stop Uber from operating in some places. Uber has also faced a lot of legal problems from its drivers and passengers. Some drivers have sued Uber, saying that they should get the same benefits as employees. Some passengers have sued Uber, saying that Uber did not protect them from sexual harassment and assault by drivers.
Worker classification
Uber considers its drivers as independent contractors, not employees, which means they do not receive benefits such as health insurance, minimum wage, or overtime pay. However, some drivers and regulators have argued that Uber drivers should be classified as employees and entitled to these benefits.
Safety concerns
Uber has been criticized for not doing enough to ensure the safety of its passengers and drivers. Some of the issues include background checks, insurance coverage, driver training, and reporting of incidents.
Unfair competition
Uber has been accused of competing unfairly with traditional taxi services by avoiding taxes, fees, and regulations that apply to them. Some taxi drivers and associations have protested against Uber and demanded that it be banned or regulated.
Competitive Pressure
Uber works in a very competitive industry, with rivals such as Lyft and Didi Chuxing trying to get more customers. Some of these competitors have big advantages, such as strong relationships with local governments and transportation companies.
Uber Financial Performance
Despite its high value, Uber has had trouble turning a profit. The company faced pressure from investors to demonstrate its ability to generate long-term profitability, leading to numerous changes in its business model and cost structure in an effort to achieve this goal. In 2022, Uber reported a net loss of $9,141 million ($-4.65 EPS). Additionally, Uber incurred a net loss of $15,770 million from 2019 to 2021.
COVID-19 Pandemic
These issues damaged Uber’s reputation, leading to the departure of key executives, including CEO Kalanick, in 2017. Financially, Uber struggled to achieve profitability and sustainability.
But despite these challenges, Uber remains a popular and highly valued company, with a market value of over $100 billion as of November 2023. Uber continues to innovate and improve its services to meet the changing needs and preferences of its customers.
Uber has hired a new CEO, Dara Khosrowshahi, who has focused on restoring the trust and confidence of the stakeholders by apologizing for mistakes, resolving disputes, and reforming the culture.
Uber has also streamlined its operations, cutting costs, selling unprofitable businesses, and focusing on its core markets and services. And it also continued to pursue its vision and mission, which is to make transportation as reliable as running water everywhere and for everyone.
Uber’s big IPO in 2019 was a huge deal in Silicon Valley. They set the price for each share at $45, and they got $8.1 billion from the IPO. After going public, Uber focused on making money, and they bought some other companies to help with that.



